This Cool Investing Feature Is the Key to Reaching Your Goals

What you'll learn
- Why you should be thinking about "future you" today
- Why being young is actually your biggest advantage as an investor
- How compound growth can boost your savings
- Why you should be thinking about "future you" today
- Why being young is actually your biggest advantage as an investor
- How compound growth can boost your savings
The Power of Investing
When you're young, it can feel like there's a whole list of things you can't do yet.
But did you know that right now—when you're in your teens—is actually the best time to start saving for your financial future?
You might be thinking, My financial future?? But I haven't even graduated from high school yet!
Well, that's sort of the point. The younger you are, the more time your money has to benefit from something called compound growth. But only if you invest it.
Compound growth: growth on top of growth
When you invest money, you're buying stocks, bonds, or other things that you think will be worth more money over time. Picking your investments might seem overwhelming, but it doesn't have to be complicated. You can choose individual investments if you want to, or you can go with something called a fund, which is a single investment that holds multiple investments within it.
Common types of investments
| Stocks | Buying a share of stock is like buying a tiny piece of the company. Its value can rise or fall. |
| Bonds | Buying a bond is like giving a loan to a government or company. They pay you regular interest until they return your money. |
| Index Funds | An index fund is an investment that buys the stocks or bonds that make up a market index, like the S&P 500®. Instead of buying individual stocks or bonds, you can buy a single index fund that holds dozens or hundreds of investments. |
When your investments make money, the result is called an investment gain, which is the difference between what you paid and what the investment is worth today. (An investment loss is the opposite: when an investment you own is worth less today than what you paid.)
If you keep those gains invested—in addition to your original money—you can potentially see your gains earn gains, too. By reinvesting those gains again and again, the process keeps repeating itself, and it can add up fast. This is the beauty of compound growth.
And remember how we said that being young is awesome for investing?
Your age is your superpower when it comes to compound growth. Even if you start with small amounts now, your money can increase exponentially if you leave it invested long enough.
Your age is your superpower when it comes to compound growth.
Confused a little? Let's clear things up with an example.
Starting early for the win
This is the story of two investors, Maria and Anna.
Maria started saving for retirement at age 25 when she got her first job. She was consistent with her contributions, adding $5,000 each and every year until age 70—saving a total of $225,000.
Anna, on the other hand, had a lot of credit card debt and some student loans to pay off, so she didn't start saving until she was 45. To try to catch up, she decided to save $10,000 a year. By age 70, she saved $250,000—$25,000 more than Maria.
Now, assuming their savings both grew by 6% each year, who do you think had more money when they turned 70?
Spoiler: It was Maria!
Even though she contributed less total money, Maria's investment balance at age 70 was $1,127,540, compared to Anna's $581,564. That's almost twice as much.
While that doesn't seem possible, it is! By starting early, Maria's money had 20 extra years for compound growth to work its magic.
Time = money
Still not convinced?
Here's a look at Maria's savings, broken down by her own contributions versus the growth those contributions earned over time.
The power of compounding
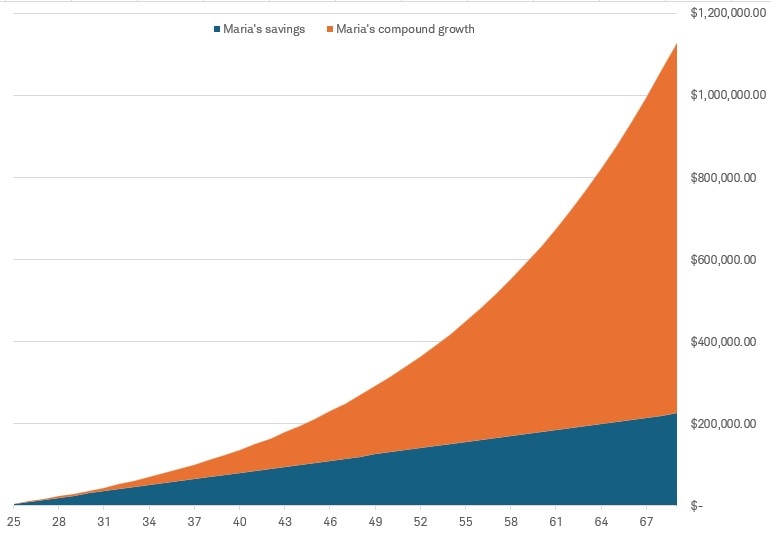
Past performance is no guarantee of future results. This chart is hypothetical and only for illustrative purposes. It is not intended to represent a specific investment product, and investors may not achieve similar results. Example assumes Maria invests $5,000 annually from ages 25 through 69, and that her portfolio grows 6% annually. Dividends and interest are assumed to have been reinvested. It does not reflect the effects of fees or taxes. Had fees, expenses, or taxes been considered, returns would have been substantially lower.
Start now!
We're big believers that it's never too soon to start thinking about your financial future. Because the earlier you get going, the more likely it is that you will reach your financial goals.
Quiz
1. True or false? You should wait to invest until you're making a lot of money.
Answer: False | As we saw with Maria and Anna, starting early with a smaller amount was way more powerful than starting later with a bigger amount. That's because the earlier you start, the longer your money has to potentially grow. On the flip side, if you start late, you might need to save a lot more money each year to reach your goal.
2. What's an investment gain?
A. The total amount of money you invest
B. When an investment you own is worth more than what you paid
C. When a stock you own is expected to grow through the roof
Answer: B | Investment gains are one way to make money from your money. For example, if you buy a $100 stock and it grows 6%, your investment gain is $6. But remember, your investment can lose money, too!
3. Compound growth happens when:
A. You invest all your money in a hot new stock
B. You try to learn a bunch of new skills all at once
C. Your money earns money, and then that new money earns money, and on and on
Answer: C | Every dollar you invest has the potential to earn money. And once that dollar earns money, then your original investment plus that new money can earn money, and on and on for as long as you keep your money invested. And the more dollars you invest, the more opportunities you have to potentially benefit from compound growth.
Your next steps
- Think of a goal you have—like saving $5,000 for college in five years—and figure out how much you need to save versus earn to reach it using the Compound Savings Calculator.
- If you're working and earning a paycheck, consider saving something toward retirement each month—even if it's just a couple bucks.
- Learn more about how to start investing for your goals.